
Malaysia is a federal constitutional monarchy located in Southeast Asia. It consists of 13 states and three federal territories and has a total landmass of 330,803 square kilometers. It is separated by the South China Sea into two similarly sized regions—Peninsular Malaysia and East Malaysia. Peninsular Malaysia shares a land and maritime border with Thailand and maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, and Indonesia. East Malaysia shares land and maritime borders with Brunei and Indonesia and a maritime border with the Philippines and Vietnam. The capital city is Kuala Lumpur, while Putrajaya is the seat of the federal government. With a population of more than 30 million, Malaysia is the 44th most populous country. Malaysia is one of 17 megadiverse countries (part of a group of countries that harbor the majority of Earth’s species and high numbers of endemic species) on Earth.
Culture
Malaysia has had an interesting past and as part of the international spice route many hundreds of years ago, the country has turned into a mosaic of cultures. To understand Malaysian culture, you must first understand its people. Malays, Chinese, Indians, and many other ethnic groups have lived together in Malaysia for generations. All these cultures have influenced each other, creating a truly Malaysian culture.
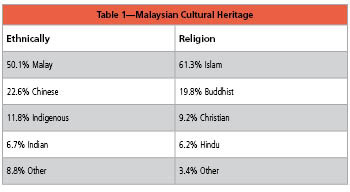
The largest ethnic groups in Malaysia are the Malays, Chinese, and Indians. In Sabah and Sarawak, there are myriad indigenous ethnic groups with their own unique culture and heritage (see Table 1).
Employment Law
The Employment Act, 1955 is the main legislation on labor matters in Malaysia. Below is a short summary of various labor issues:
Minimum Wage—RM1000 per month or RM4.81 per hour on the peninsula, and RM920 per month or RM4.42 per hour for the states of Sabah, Sarawak, and Labuan. Malaysia's minimum wage was last changed on 1 July, 2016.
Working Hours—The Malaysian Employment Act defines the workweek as 48 hours, with a maximum of eight working hours per day and six working days per week. There are special restrictions, considered to be protection provisions, for women in the industrial or agricultural sector. They are not permitted to work between the hours of 10 p.m. and 5 a.m.
Overtime Pay—For any overtime work carried out beyond the normal hours of work, the employee must be paid at a rate not less than one-and-one-half times the employee’s hourly rate of pay irrespective of the basis on which his or her rate of pay is fixed. This means that the agreed-upon workweek must be in writing and that all time worked above that agreed time is paid at the regulated overtime rate.
Type of Employees—Full-time, part-time, apprentices
Employment Contracts—Employment contracts are used in Malaysia. The employment contract must contain the following details:
- Job title
- Wages and details of other monetary payments
- Normal working hours
- Notice period prior to termination
- Retirement age
- Requirement of confidentiality and whether requirement is needed to work overtime
- Holiday and leave entitlements
- Other benefits
- Probationary period
- Exclusive service
- Mobility requirement
- Requirement to comply with company rules and penalties for misconduct
Employment contracts can be for a fixed term or an undecided term that lasts until the employment is terminated by the employer or the employee leaves voluntarily.
Income Taxes
Personal income tax filing is done annually and is due to the taxing authority by April 1 of the preceding year. Malaysia is a tax-friendly country. Income tax is comparably low, and many taxes that are raised in other countries do not exist in Malaysia.
The highest income tax rate was recently 28%, but has been reduced to 26% for residents and 27% for nonresidents. In addition, taxes like estate duties, annual wealth taxes, accumulated earnings tax, or federal taxes are not levied in Malaysia.
Additional taxes and statutory declaration requirements:
- EPF (Monthly Declarations)
- SOCSO (Monthly Declarations, New Joins)
- Tax—CP39, CP22, CP22A, CP21, Form E, EA Form, PCB 2(II)
- Human Resource Development Fund
- PTPTN1 (Perbadanan Tabung Pendidikan Tinggi Nasional)
Payment due dates: Monthly by end of preceding month
Social Insurance Programs
Time Off
Sick Leave—Where no hospitalization is necessary:
- 14 days in the aggregate in each calendar year if the employee has been employed for less than two years;
- 18 days in the aggregate in each calendar year if the employee has been employed for two years or more but less than five years;
- 22 days in the aggregate in each calendar year if the employee has been employed for five years or more; or
- 60 days in the aggregate in each calendar year if hospitalization is necessary, as may be certified by a registered medical practitioner or medical officer
Maternity Leave—Every woman is entitled to maternity leave for a period of not less than 60 consecutive days (also referred to as the eligible period) in respect of each confinement, and she is entitled to receive from her employer a maternity allowance in respect of the eligible period.
Paternity Leave—Not required
Annual Leave (Vacation)
- 8 days for every 12 months of continuous service with the same employer if the employee has been employed by that employer for a period of less than two years;
- 12 days for every 12 months of continuous service with the same employer if the employee has been employed by that employer for a period of two years or more but less than five years; and
- 16 days for every 12 months of continuous service with the same employer if the employee has been employed by that employer for a period of five years or more; and if the employee has not completed 12 months of continuous service with the same employer during the year in which his/her contract of service terminates, his/her entitlement to paid annual leave will be in direct proportion to the number of completed months of service
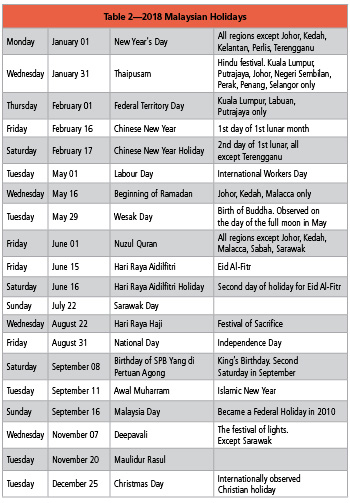
National Holidays for 2018
Malaysia has several regions, and all celebrate holidays specific to that region (see Table 2).

Dee Byrd, CPP, PHR, SHRM-CP, is a Project Manager for PayTech, Inc., who has more than 25 years of global payroll management experience and has represented the payroll profession by speaking to the U.S. Congress in matters regarding multistate payroll taxation issues. She is an American Payroll Association (APA) Vice President, a member and past chair of the APA’s Electronic Payments Committee, part of the APA’s Payroll Cards Subcommittee of the Government Relations Task Force (GRTF), a member of the APA’s Global Issues Subcommittee of the Strategic Payroll Leadership Task Force (SPLTF), and also a member of the APA’s Board of Contributing Writers. Byrd was also the APA’s 2011 Payroll Woman of the Year.