
Hungary is a parliamentary democracy located in central Europe. This land-locked country is bordered by Austria, Croatia, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, and Ukraine. Hungary consists of 19 counties, and its capital is Budapest.
Employment Start
Businesses must register with the tax authority, and both the employer and employee must register with the National Health Insurance Fund and receive a Social Security Information Number (Társadalombiztosítási Azonosító Jel or TAJ).
Information on foreign businesses is not required to register, but if the business has employees working in Hungary, they are liable for social taxes with the National Tax and Customs Administration (NTCA).
All employees must be registered with the Tax Department and the National Office for Health Insurance prior to starting work. A new hire will need to register with the tax authorities
through the National Tax Authority (NAV) at least one day before their start date and supply the required information, which includes the following:
- Full name, address, date of birth, place of birth, mother’s name
- Tax card number
- Pension insurance number
- ID number, bank account details, employer’s name, gross salary, starting date, type of contract, position, activity/job code number (FEOR)
- Exit documents from the previous employer—employment certificate, certificate about contributions paid, salary and income tax certificate, certificate for unemployment allowance, social security booklet, certificate about maintenance obligations established through judicial decision
Employers must supply a written employment contract within 15 days of the start of employment. Both parties must agree on the personal base wage and the position of the employee.
There are two main types of employment contracts, which include the following:
- Fixed term (határozott időre szóló munkaszerződés): Cannot exceed five years, but can be extended for a six-month period
- Indefinite (határozatlan időre szóló munkaszerződés): Used for permanent employees
Probationary periods cannot be more than three months from the employee’s start date.
The standard work week in Hungary is five days, 40 hours per week, Monday to Friday, and a work day is typically eight hours a day.
Work can usually not exceed 12 hours per day and 48 hours a week.
Work above standard working hours is paid as overtime and regulated by employment contract/collective agreements, but employers can agree to overtime arrangements directly with workers or negotiate with unions.
Employers are allowed to require employees to work up to 400 hours of overtime per year.
Overtime pay is due when more than eight hours per day are worked on a normal working day and is calculated at 1.5 times normal pay. Overtime worked on rest days can be paid at the same rate if an alternative rest day is given or paid at double time without a replacement rest day.
Work performed on a holiday must be paid at double time. Night work must be remunerated at 115% of normal pay after the first hour and is defined as work performed between 10:00 p.m. and 6:00 a.m.
Employers must give one rest day each week but usually give two.
The payroll frequency is monthly, with work between the first and last day of the month typically paid on the last day of the month but must be paid by the 10th of the following month. Employers may supply payslips online and must keep payroll reports for at least seven years.
Compensation, Benefits
Employers must adhere to the Labor Code relating to compensation and benefits policies and practices. The code covers standards about minimum wage, overtime, hours of work, paid holidays, paid leave, and other benefits, including termination pay.
The Labor Code regulates labor affairs and is administered by the Ministry of Innovation and Technology.
There is no requirement for employers to pay a bonus and a 13th month salary is not mandatory.
Leavers, Termination Pay
Fixed-term contracts can be terminated for business or personal reasons or for worker misconduct.
Upon termination of the employment relationship by notice, the employee must receive the final payment no later than the fifth working day after the last day of employment, with a T1041 document (Registration Form for Leavers) that must be completed and returned to the NTCA.
Employees are entitled to their average earnings during the notice period and severance pay if they are not of pension age.
Severance pay is due if the employer terminates employment for operational reasons. The amount of severance pay is a minimum of one month’s salary and a maximum of six months, dependent on the employment contract.
The notice period can be extended depending upon the employee’s length of service, so that after three years of service, 35 days’ notice is required, increasing up to a maximum of 90 days after 20 years of service.
The Labor code prohibits employers from ending the employment by ordinary notice if an employee is unable to work due to illness, and during a maximum of the one-year period following the expiration of the sick leave period.
National Minimum Wage
The standard national minimum wage (NMW) is also referred to as the unskilled worker minimum wage. The minimum wage for employees working in positions that require an advanced degree or training is referred to as the skilled worker minimum wage and the guaranteed wage minimum. The rates are set in January each year.
Income Taxes
Employers must withhold income taxes from employees' pay. The residency status of employees in Hungary may affect the amount of income tax due. Tax residents are charged for all worldwide income, while nonresidents are only charged for income sourced within Hungary.
Employees are subject to personal income taxes at a flat rate of 15% but benefits in kind are taxed separately, and pension contributions are exempt from income tax.
From January 2022, employees younger than 25 years old do not pay personal income tax.
Social Taxes
Employers must withhold social security contributions from employees' pay and make additional payroll-related contributions to Hungary's social programs. Social security, health insurance, and unemployment insurance are funded through mandatory employer and employee contributions in addition to government funds.
Employees can make additional voluntary contributions to old age pension benefits.
Employees and their employers may also pay into a voluntary pension fund.
Time Off
Hungary requires employers to provide paid leave, sick leave, maternity leave, paternity leave, parental leave, care leave, and education leave.
Vacation Leave
.png?sfvrsn=245763e7_0) Employees are entitled to 20 days of paid leave per year. Leave increases depending on their age, increasing the year they reach the relevant age, as follows in Table 1.
Employees are entitled to 20 days of paid leave per year. Leave increases depending on their age, increasing the year they reach the relevant age, as follows in Table 1.
Employees (one parent) with children under 16 years of age are also entitled to extra vacation time as follows:
- Two working days for one child
- Four working days for two children
- Seven working days for three or more children
In addition to the above, employees are entitled to additional supplementary leave in certain cases. The Labour Code specifies the following types of supplementary leave:
- Young workers—workers bringing up a child under 16 years of age
- Workers working underground on a permanent basis
- Workers spending at least three hours a day in a workplace exposed to ionising radiation
- Fathers for the birth of a child
- Disabled workers
- People entitled to disability benefits or benefits for the blind
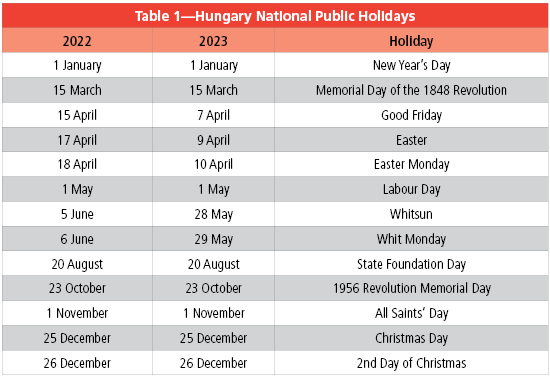
Public Holidays
Depending on which day of the week a bank holiday falls, the previous or the following day is deemed to be a “rest day” to make a long weekend for employees. In these cases, Saturday is usually declared a working day instead to keep the number of workdays the same during the year.
Table 2 includes all public holidays recognised by Hungary.
Maternity, Adoption Pay/Leave
Employees receive 24 weeks of maternity leave starting four weeks before the employees' due dates but can take up to three years of leave and receive maternity benefits.
For the first 168 days, mothers are entitled to a Pregnancy and Confinement Benefit (CSED) at a rate of 100% of the salary and only personal income tax is deducted from this amount. For the next 18 months, until the child’s second birthday, mothers are entitled to a Child Care Fee (Gyermekgondozási díj – GYED) paid at 70% of the salary up to a maximum of double the minimum wage. The benefits are paid by the National Health Insurance Fund of Hungary (NEAK).
Paternity Leave/Pay
Employers must give male employees five days of paid leave if one child is born and seven days of paid leave if more than one child is born to be taken in one or several parts within two months of the date of birth of the first child. Any income and taxes related to this period are reimbursed to the employer by the State Treasury.
Parental Leave
After the maternity leave period, one parent can take parental leave until the child reaches two years old. This is paid at 70%, capped at double the minimum daily wage.
Employees are entitled to unpaid leave for the following:
- Until the child reaches the age of three years old for childcare, including managers
- While they are in receipt of the childcare benefit or child allowance, up to the child’s 10th birthday
- To care in person for a relative requiring permanent care, for up to two years
- For the duration of voluntary military reserve service
A benefit, Child Home Care Allowance (Gyermekgondozási segély – GYES) is available for parents or grandparents taking care of a child up to the age of three years.
Care Leave
Employers must give employees—if requested—unpaid leave to care for children under 10 years old or for the care of a close relative that the employee is personally providing all the care.
Education Leave
Employers must give employees the following unpaid time off to take exams or work towards a diploma:
- Exam Leave—four days per exam taken
- Diploma Leave—10 days to complete work towards a diploma
Paid Sick Leave
Employees are entitled to 15 days of sick leave per year paid by the employer at a rate of 70% of the salary. From the 16th day up to one year (unlimited for a work accident), the payment varies between 50%-60% depending on the term of service. One-third of the payment is paid by the employer and two-thirds are paid by the National Health Insurance Fund.
Keeping Records, Reporting
Employers must use the Cégkapu online portal for electronically transmitting and receiving documents and correspondence from the government and for communications with the NAV.
Employers must submit social tax information electronically through the e-NYENYI online system to the NTCA.
Returns regarding data for a month are due by the 12th day of the month following the reported month.
Tax and social tax records must be kept for a minimum of five years, and employers must keep records of employees’ working hours, on-call, and standby time, overtime, and leave, with no time limit specified for retention.