
Ecuador is known for its beautiful landscapes, wildlife and, of course, the Galapagos Islands. More and more companies are setting up operations there, particularly in the capital of Quito. It is important that employers know the basics about operating payroll in this beautiful country prior to hiring. Here are key aspects to be mindful of:
Is local registration required? If so, what is the deadline?
Yes, when a company has a new employee, it must inform the Ecuadorian Institute of Social Security (IESS) and the Ministry of Labor. The company has 30 days to report.
What is the list of documents that need to be provided for the registrations?
The following documents are needed:
- Employment contract, signed by a legal representative and the employee
- ID—the personal identification in Ecuador
- Basic service or utility bill/invoice containing employee address
- Employee disability certificate
- IESS code, if the employee is a foreigner
Complete personal information of the employee is needed in addition to the above. These documents are needed, if applicable:
- Marriage certificate
- Birth certificates of children under age 18
- Certificate of disability of dependents
Does the employer need to keep the employee files physically at the office or may the files be stored electronically?
It is important to keep the physical information at the company office.
Is de-registration required? If so, what is the deadline?
Yes, when the company has a termination, it must inform IESS and the Ministry of Labor. On the Ministry of Labor website, the employer has to issue the legal document for terminations. It has 30 days to report any change.
What is the list of documents needed for de-registration?
Only the legal document issued by the Ministry of Labor (from the website) signed by the legal representative and the employee is needed for de-registration. The employee must also send a letter or an email with the decision to terminate the employment contract. This should be on record.
Risks Associated With New Hire, Termination Process
New Hires
IESS—If the company has late registration, the company could report for the next three months, but with a fine of 4% over the employee´s salary. If the company does not report in 90 days, it must raise a request to IESS and work through an official process as issued by the IESS.
Ministry of Labor—There is no specific fine. However, if the company does not manage the upload of the employee information, it can´t make the termination file (finiquito) or report changes in salary.
Terminations
IESS—If the company has a late registration, the company will pay social security for the period of time it does not report the termination. It will be an additional cost for the company, and not deductible.
Ministry of Labor—There is no specific fine.
Vacation Days
Are vacation days processed via payroll on a monthly basis?
In Ecuador, employees have 15 days of vacation, including weekends (11 business days). If the employee takes vacation, the employer has to enter the days taken.
What are the rules for processing vacation days?
The vacation provision is calculated each month, based on the employee’s salary, extra time worked, bonus, and other income. That means all income for the employee is divided by 24. Days are calculated in dates proportionally during the year.
Are any accruals processed via payroll for vacation days?
Yes. Every month, the employer has to make the provision and keep a detail of the days taken and days pending.
Do employees need to provide any paperwork for requesting vacation days? If so, does it need to be wet signed (employee signature required)?
Yes, for better control, employees must send an email or a signed letter with the request and approval of their superior for the vacation days to be taken.
Are there any extra months that need to be processed via payroll (e.g., 13th month)?
During the year, the employer must prepare information for the 13th salary, the 14th salary, income tax withholdings for employees, and employees with profit sharing.
What are the accrual rules and when are those paid?
- 13th salary—All employee income during the year divided by 12 months is additional salary. The company must pay employees no later than December 24.
- 14th salary—A fixed amount for the employee of US$ 400 (for 2020). The amount changes each year. The company must pay employees no later than August 15.
- Income tax withholdings for employees—A report to the Ecuadorian Internal Revenue Service or Servicio de Rentas Internas (SRI) with information on employee withholding taxes. The company must make withholdings for employees every month based on a table and pay SRI every month. The annual report (YTD) that the employer/provider has to present in January to the SRI.
- Employees with profit sharing—This is a report the employer has to submit to the Ministry of Labor. The calculation is based on 15% of the company's earnings in the year. This amount must be paid in April by the company to the employees.
Is the annual salary divided by 12?
Yes.
What are the pro-ration rules/formula in the event that an employee does not receive a full salary for the month?
The employer must consider 30 days for a month in any case.
Tax and Social Security
Social security—The company must pay 12.15% of all employee earnings, and it is the cost of the company. The employee must pay 9.45% for all employee earnings. The discount and payment to IESS is monthly.
Withholding of income tax for employees—The company withholds the income tax of the employee on all income except authorized personal expenses. The base is US$11,315 during the year (see Table 1).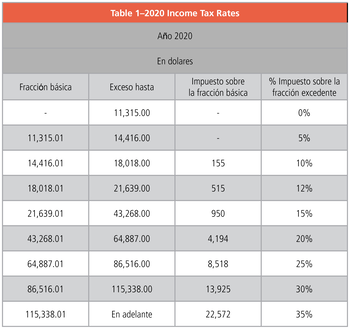
What elements are exempt from tax and social security?
Only refunds to employees.
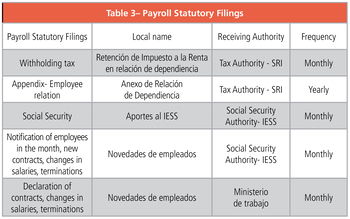
When are contributions to be paid to the different authorities?
See Table.
What are the different types of overtime paid and the rules associated with them?
Overtime, after normal hours, is set at a maximum of four hours per day and 12 hours per week; there is a 25% surcharge on salary. If the employee works until midnight, he or she has a surcharge of 50% of salary, and if the work is between midnight and 6:00 a.m. the next day, the surcharge is 100%.
How is overtime calculated?
The calculation is monthly salary divided by 240 (8 hours per 30 days) multiplied by 25% or 50% or 100% multiplied by the number of hours of overtime.
How is the hourly rate of the employees calculated?
It is the monthly salary divided by 240 (8 hours per 30 days).
Are there any legal increases that need to be processed throughout the year? If so when? What are the calculation rules/basis in law?
Normally, the increases are once a year. In private companies the amount only depends on the decision of the company. In January, the government announced an increase in the basic salary. For 2020 it is US$400.
Are there any legal increases resulting from union agreements?
No, there are no increases from union agreements. In Ecuador the union agreements have almost disappeared.
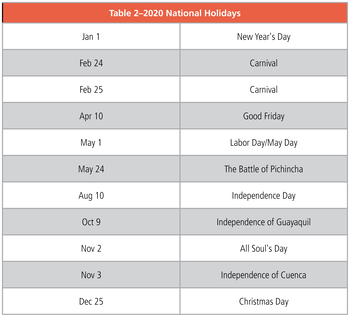
What are the national holidays in Ecuador?
See Table 2 for Ecuador’s observed national holidays.
Do you like our content? Join the GPMI community to get free education and articles straight to your inbox!

Auxadi provides International expansion services under a single IT platform as One-Stop-Shop solution in accounting, tax compliance and payroll. From its HUBS in Chicago & Madrid, with over 40 years of experience, 250 employees, 10 intl offices, its Intl Desks and its cloud platform, Auxadi helps more than 1000 US & European corporations expanding abroad.